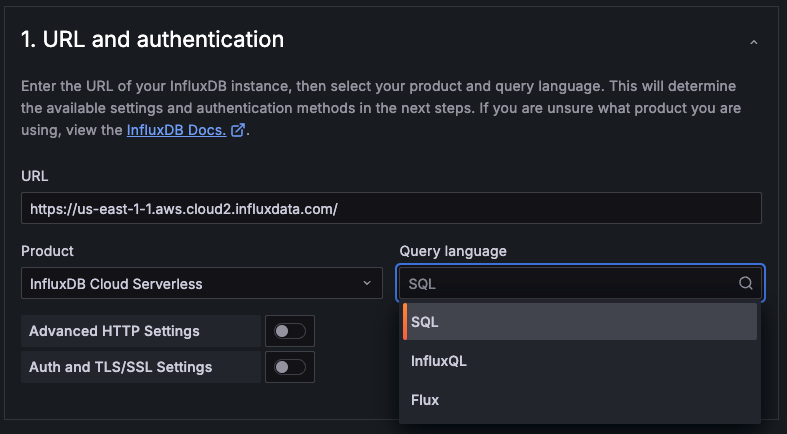
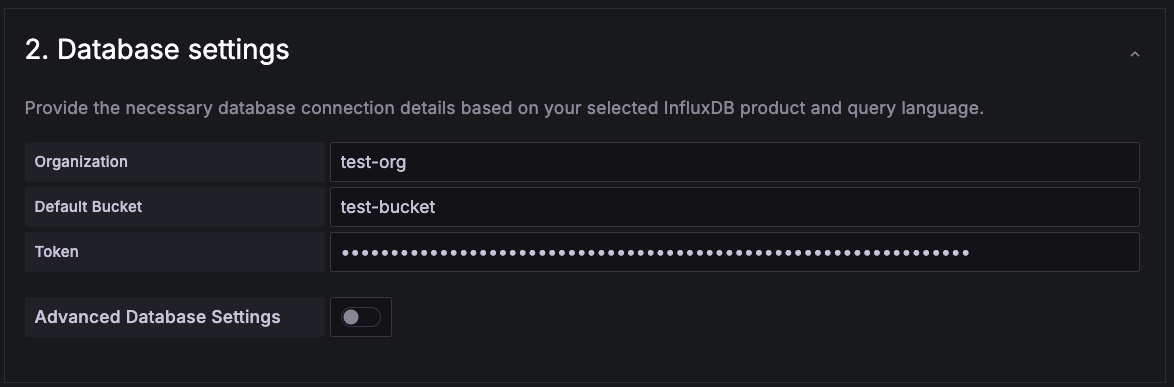
#44449-externalize-configuration
#44449-fix-context
#44449-fix-rendering-service-is-available
#44449-image-render-doc
#44449-image-renderer-musl-build
#45498-fs-config
#45498-fs-object-storage
#45948-entity-events-trigger
100096/metrics-drilldown-route-guard
100296/update-explore-metrics-to-metrics-drilldown
101011-docs-document-new-alerting-threshold-operators
102280-move-footer-options
102431-move-wrap-text-options
103161-fix-table-ng-inspect
1036-docs-add-documentation-for-alert-rule-history
103652-docs-alert-migration-tool
105079-docs-missingseries-alerting-docs
105977-allow-gropby-aggregation
106188-alerting-docs-best-practices-edit
106386-alerting-docs-note-about-pdc-on-recording-rules
107480-alerting-docs-typo
11818-percent-calc
12.0.1-fix-team-membership
12.0.1-k8s-cleanup-dash-folder-endpoints
12.0.2-manual-backport-org-fix
14078-support-request---updating-an-existing-public-document---alerting---httpsgrafanacomdocsgrafanalatestalertingfundamentalstemplates
14395-support-request---updating-an-existing-public-document---alerting---httpsgrafanacomdocsgrafanalatestsetup-grafanaconfigure-grafanaunified_alerting
20230331_add_kerberos_support
2025-mar-19-update-annotations-api
2025.06.18_FixURLS
20250219_add_react_dev_resolver_for_docker
20250716_add_react_dev_resolver_for_docker
86870-canvas-pan-and-zoom
89510/native-histogram-banner
92184-legend-colours
92337-datalinks-dnd
94621-alerting-docs-update-gma-note
94778-column-width=parity
95188-table-styles-to-linaria
98279-update-grafana-versionrelease-link-on-login-page-to-the-whats-new-doc
98725/translation
99111/prom-bundler-mode
AWierzbicki/#41993-live-perf-tests
Elastic_RQE
IfSentient/register-only-one-internal-kind
JayEkin-patch-6
SCIM-add-reloadable-api-config
Vizards
academo/levitate-pipeline-fix-2
academo/sandbox-docs
academo/test-levitate
academo/test-levitate-comment-to-slack
academo/test-levitate-optional-parameter
academo/test-levitate-optional-parameter-part2
access-control-fix-default-permissions
access-metrics
access_kv_delete
adapter-test
add-authz-stubs-marshall-metadata
add-canonical-explore-metrics
add-cssglobal-themevars
add-current-rv
add-df-resource
add-full-pr-check-for-docs
add-gcr-to-icon-list
add-git-prefix
add-icon-support
add-idtoken-to-backend-user
add-local-grpc-authenticator
add-memory-backend
add-metadata-to-grpc-logging
add-plugins-auto-update-feature-main
add-rv-to-index-and-search-result
add-secondsToLive-in-add-token-api
add-secret-service
add-structure-metadata-to-alert-state-history
add-transformations-learning-journey
adding-elements-rethink
adding-webhook-stub-view
addon-sidecar-app
addonbar
adela/actions_auth
adela/canvas_tooltip_option
adela/chore_canvas_warnings
adela/chore_table_utils_refactor
adela/datalinks_one_click
adela/decouple_hide_from
adela/expose_hidden_fields
adela/fix_state_timeline_duration
adela/one_click_data_links
adela/table-ng_actions_support1
adela/table-ng_datalinks_support
adela/table_actions_context_menu
adela/table_hover
adhoc-filters-variable
advisor-registry
advisorNewAppSDK
agnestoulet/add-e2e-enterprise
agnestoulet/docs-rendering-rate-limiter
agnestoulet/pdf-update-zoom
agnestoulet/report-image-customizations
alert-autofix-940
alerting-pkg-part-2
alerting-pkg-tsdown
alerting/add-cp-filter-in-alert-rule_TR
alerting/ai-buttons-improvements
alerting/ai-feedback-about-llm-response
alerting/alert-rule-detail-routing
alerting/alert-rule-versions-1_TR
alerting/alerting-app-sdk-TR
alerting/ash-panel
alerting/better-search-2
alerting/bulk-actions-part1_TR
alerting/bump-app-sdk-version
alerting/cache-bust-preview-routing
alerting/cash-improvements
alerting/consolidate-datasources
alerting/contact-point-creation-alert-rules
alerting/enrichment-ui
alerting/exposed-component-test
alerting/filter-contact-points
alerting/fix-evaluation-interval
alerting/fix-no-search-results-loop
alerting/fix-sub-url-datasourcepicker
alerting/hackathon-2024-12-alerting-oncall-simplified
alerting/improve-performance-in-alert-list-panel
alerting/improved-filters
alerting/jest-project
alerting/labels-autocomplete
alerting/list-v2-empty-states
alerting/list-view-v2-minor-fixes
alerting/llm-experiment
alerting/loki-recording-rule-fixes-tests
alerting/msw-scenarios
alerting/no-unused
alerting/notification-templates-list-view
alerting/omit-title-from-alerting-wrapper
alerting/pkg-add-testing-target
alerting/poc-identifiable-cloud-rules
alerting/prometheus-pagination
alerting/recording-rules-paused
alerting/rxjs-consistency-check
alerting/scenarios-setup
alerting/storybook-root
alerting/support-unknown-rule-state
alerting/translation-markup
alerting/use-BE-filter-for-labels-in-ash
alerting/use-k8s-routes-api_TR
alerting/user-event-cleanup
alerting/wrap-strict-mode
alerting_is_equal
alexander-akhmetov/add-alert-rule-group-to-state
alexander-akhmetov/add-namespace-uid-to-rule-group-key
alexander-akhmetov/alert-rule-conditional-reset
alexander-akhmetov/alert-rule-conflict-error
alexander-akhmetov/alerts
alexander-akhmetov/alerts-metric
alexander-akhmetov/alerts-writer-ff
alexander-akhmetov/am-merge
alexander-akhmetov/backoff
alexander-akhmetov/cortextool-path
alexander-akhmetov/datasources-http-options
alexander-akhmetov/delete-reason
alexander-akhmetov/fail-on-internal-am-errors
alexander-akhmetov/gen-ai-rule-editor
alexander-akhmetov/gen-rule-ids-experiment
alexander-akhmetov/get-annotations
alexander-akhmetov/instance-store-alert-rule-with-group
alexander-akhmetov/mqtt-append-group-key-to-topic
alexander-akhmetov/mt
alexander-akhmetov/mt-folders-lock
alexander-akhmetov/mt-folders-service
alexander-akhmetov/mt-lock
alexander-akhmetov/mt-stable-api
alexander-akhmetov/mt-template
alexander-akhmetov/mt-template-ast
alexander-akhmetov/mt-template-prometheus-mode
alexander-akhmetov/mt2
alexander-akhmetov/parallel-full-state-sync
alexander-akhmetov/prometheus-rule-group-fields
alexander-akhmetov/provenance-upsert-2
alexander-akhmetov/rule-group-in-state
alexander-akhmetov/rule-lifecycler
alexander-akhmetov/sanitize-labels
alexander-akhmetov/save-alert-instances
alexander-akhmetov/save-alert-instances-for-rule
alexander-akhmetov/save-extra-configs-on-am-updates
alexander-akhmetov/single-alert-type
alexander-akhmetov/state_annotations_lock
alexander-akhmetov/swagger
alexander-akhmetov/unskip-test
alexander-akhmetov/update-alerts-on-folder-move-event2
alexander-akhmetov/upgrade-prometheus-alertmanager
alexjonspencer1/betterer-updates
alexjonspencer1/canvas-panel-key-issue-fix
alexjonspencer1/dataviz-test-coverage
alexjonspencer1/fieldReducer-test-refactor
alexjonspencer1/fix-footer-bug
alexjonspencer1/fix-table-cell-hover-behaviour
alexjonspencer1/front-end-test-coverage-github-action
alexjonspencer1/minor-table-ng-refactor
alexjonspencer1/playwright-visual-regression-testing-prototype
alexjonspencer1/prototype-two-phase-datagrid-init
alexjonspencer1/sql-expressions-ai-hackathon-prototype
alexjonspencer1/sql-expressions-discovery-prototype
alexjonspencer1/sql-expressions-drawer-architecture
alexjonspencer1/sql-expressions-event-tracking
alexjonspencer1/sql-expressions-helper-text-update
alexjonspencer1/table-ng-bugfix-imagecell
alexjonspencer1/table-ng-column-width-updates
alexjonspencer1/table-ng-fix-bottom-summary-cell-style-clash
alexjonspencer1/table-ng-footer-g12
alexjonspencer1/table-ng-footer-styles
alexjonspencer1/table-ng-hide-area
alexjonspencer1/tableng-bugs
alexjonspencer1/tableng-configure-bottomSummaryRows
alexjonspencer1/tableng-displayedValue-as-null
alexjonspencer1/tableng-subtable-sorting
alexjonspencer1/viz-regression-testing-poc
alexweav/log-execution
alexweav/nil-no-data
alexz/zanzana-refactor-check
alexz/zanzana-refactor-serverside
allow-provision-to-override-autoenabled
allow-testing-db-only-from-integration-tests
alternative-operation-id
always-take-most-specific-timerange
alyssa/azure-logs-builder-template-variables
alyssa/fix-opentsdb-queries-with-diff-time-ranges
alyssa/influx-chart-loss
alyssajoyner-patch-1
andre/fix-grpc-change
andre/node-graph-stuff
andreas/azmon-test
andreas/fix-swagger
andreas/fix-time-selector
andreas/influx-dashboard-repro
andreas/update-npm-publish
andrew/aws-prom
andrew/azure-logs-default-change
andrew/cloud-prom-support-import-dashboards
andrew/cloud-prom-support-import-dashboards-2
andrew/graphite-compare-query-builder
andrew/graphite-lexer-add-at-sign
andrew/prom-type-migration-service
aocenas/extension-test
aocenas/folders/migrate-api-2
aocenas/query-library/data-migration
api-client/process-spec-be
api-validation-tests-enable-mode3
apis/plugins
apis/plugins-backup
apiserver-iam-ext
app-platform-wg-206/cleanup-dashboard-via-k8s-delete
appchrome-side-pane
apps/plugins
apps/plugins-restconfig
area-git-sync
ariatron-whitelabel-update
arunkg2787-patch-1
ash/body-scrolling-safari
ash/colorblind-themes
ash/config-editor-fix-i18n
ash/expose-lint-rule
ash/fix-geomap-tooltip
ash/fix-lefthook
ash/fix-tooltip-positioning
ash/fix-tooltip-positioning-2
ash/hacky-react-19
ash/i18n-markup-8
ash/layout-tweak
ash/megamenu-arrows
ash/menu-padding
ash/offset-border-radius
ash/react-19
ash/reusable-upload
ash/scroll-container-poc
ash/scss-cleanup-12
ash/single-top-nav-alerting
ash/single-top-nav-banners
ash/speedy-emotion-hack
ash/theme-css-vars-hack
ash/theme-json-schema
ash/zizmor
auth/bump-authlib
authn/cleanup-api-key
authn/grpc-authenticator
authz-dashboard-folder-remove-featureflag
authz/service
auto-gen-fix-panel-state-issues
auto-grid-remove-defaults
auto.empty-state
automation-labels
axelav/QL-open-in-explore
axelav/add-queryref-to-explore
axelav/annotation-angular-support
axelav/play-panel-search-behaviour
axelav/poc-arbitrary-element-identifiers
axelav/test-clone-deep-scenes
axleav/play-branch-panel-search-behavior
backport-100144-to-release-10.4.17
backport-100144-to-release-11.5.2
backport-100352-to-release-11.5.2
backport-100496-to-release-11.1.12
backport-100657-to-v10.4.x
backport-101096-to-release-11.5.3
backport-101475-to-release-11.5.3
backport-101637-to-release-10.2.91
backport-101679-to-release-11.5.3
backport-101814-to-release-11.4.3
backport-102182-to-release-11.3.5
backport-102587-to-release-11.4.3
backport-102780-104316-104381-to-release-12.0.1
backport-104087-to-release-11.6.2
backport-104193-to-release-12.0.1
backport-104195-to-release-12.0.1
backport-104308-to-release-12.0.1
backport-104427-to-release-12.0.1
backport-104433-to-release-12.0.1
backport-104827-to-release-11.1.14
backport-104931-to-release-11.6.2
backport-105607-to-release-11.6.2
backport-105607-to-release-12.0.1
backport-105748-to-release-11.3.7
backport-106060-to-release-11.5.6
backport-106060-to-release-11.6.3
backport-106060-to-release-12.0.2
backport-106375-to-release-12.0.2
backport-106440-to-release-12.0.2
backport-107911-to-release-12.1.0
backport-15025222693-to-main
backport-15025385581-to-main
backport-15026397893-to-main
backport-15159155368-to-main
backport-15159155392-to-release-11.2.10
backport-6867-to-v11.0.x
backport-7293-to-v11.2.x
backport-88182-to-v11.1.x
backport-89619-to-v11.1.x
backport-89751-to-v11.0.x
backport-89790-to-v11.1.x
backport-90008-to-v11.1.x
backport-90069-to-v9.4.x
backport-90146-to-v11.0.x
backport-90146-to-v9.5.x
backport-90588-to-v11.0.x
backport-90588-to-v11.1.x
backport-90816-to-v11.1.x
backport-90907-to-v11.1.x
backport-91204-to-v11.0.x
backport-91767-to-v11.2.x
backport-91977-to-v11.2.x
backport-92201-to-v10.4.x
backport-92201-to-v11.0.x
backport-92374-to-v10.3.x
backport-92462-to-v11.0.x
backport-92862-to-v11.2.x
backport-92886-to-v11.1.x
backport-94517-to-v10.2.x
backport-94846-to-v11.3.x
backport-94846-to-v11.3.x-copy
backport-95003-to-v11.0.x
backport-95003-to-v11.1.x
backport-95003-to-v11.2.x
backport-95003-to-v11.3.x
backport-95418-to-v11.3.x
backport-96711-to-v11.3.x
backport-96825-to-v11.3.x
backport-97197-to-v11.3.x
backport-98487-to-v11.4.x
backport-98510-to-v11.4.x
backport-98590-to-v10.1.x
backport-98590-to-v10.2.x
backport-98661-to-v11.4.x
backport-98808-to-v11.4.x
backport-98834-to-release-11.5.2
backport-99333-to-v11.3.x
backport-99496-to-v11.2.x
backport-fix-unistore-connection-string
backport-upgrade-scenes-package-to-v11.3.x
backport106955_v114
baldm0mma/add_cert_check
baldm0mma/backport_validation
baldm0mma/legend
baldm0mma/rem_tests
baldm0mma/test_backend
baldm0mma/update_gha_ver
baldm0mma/update_version_and_workspace
baldm0mma/update_wn_url
baldm0mma/verify_npm
banner/move-to-oss
batch-index-creation
bergquist_update_tempo_ref
bleve
bleve-authz-stub
bleve-indexing-test
bleve_poc
bogdan/conditional-rendering-improvements
bogdan/dashboard-banners
bogdan/fix-v2-annotations
bohandley/add-logging-to-select-component
bohandley/em/fix-otel-bug
bohandley/expose-add-to-dashboard
bohandley/link-from-alerts-to-drilldown-app
bohandley/prometheus-add-error-for-status-not-2XX
bohandley/prometheus-fix-met-exp-classic-hist-type
bohandley/prometheus-remove-old-regex-multi-variable-checks
brojd/registrar-example
bump-version/14071548414/12.0.0
canvas_actions
canvas_links_actions_ux
change-default-access-client
changelog/10098116837/11.1.1
changelog/10098370388/11.1.1
changelog/10098407314/11.1.1
changelog/10098752747/11.1.1
changelog/10098868040/11.1.1
changelog/10098942112/11.1.1
changelog/10098987623/11.1.1
changelog/10099015406/11.1.1
changelog/10100644002/11.1.1
changelog/10100684153/11.1.1
changelog/10100797766/11.1.1
changelog/10101103482/11.1.1
changelog/10101187064/11.1.1
changelog/10101890568/9.5.21
changelog/10102112651/9.5.21
changelog/10102350594/9.5.21
changelog/10102468667/9.5.21
changelog/10102584715/9.5.21
changelog/10102650044/10.2.9
changelog/10102792273/10.2.9
changelog/10102857047/10.2.9
changelog/10102948117/10.4.6
changelog/10103002725/11.0.2
changelog/10104494648/11.1.2
changelog/10104504884/11.1.2
changelog/10112541950/11.1.3
changelog/10118284765/11.1.3
changelog/11382147019/11.0.5+security-01
changelog/11382582831/11.0.5+security-01
changelog/11384984776/11.0.5+security-01
changelog/11385224277/11.0.5+security-01
changelog/11385297718/11.0.5+security-01
changelog/11385710935/11.0.5+security-01
changelog/11385963777/11.0.5+security-01
changelog/11386309680/11.0.5+security-01
changelog/11386417537/11.0.5+security-01
changelog/11386711801/11.0.5+security-01
changelog/11390495637/11.2.2+security-01
changelog/11391162998/11.1.7+security-01
changelog/11464720998/11.3.0
changelog/11798304752/11.3.0+security-01
changelog/11799132767/11.3.0+security-01
changelog/11799291799/11.3.0+security-01
changelog/12167153824/11.3.2
changelog/13388904127/10.4.16
changelog/13389548070/10.4.16
changelog/13395688804/11.0.11
changelog/13396914711/10.4.16
changelog/13400427896/11.3.4
changelog/13400795059/11.3.4
changelog/13401021557/11.3.4
changelog/14841584418/12.0.0
changelog/14842070615/12.0.0
changelog/14842665582/12.0.0
changelog/15164321327/10.4.18+security-01
changelog/15164950411/11.2.9+security-01
changelog/15165786792/11.3.6+security-01
changelog/15166228059/11.4.4+security-01
changelog/15166918811/11.5.4+security-01
changelog/15167349249/11.6.1+security-01
changelog/15190633732/10.4.19
changelog/15190828919/10.4.19
changelog/15190963038/10.4.19
changelog/15191179155/10.4.19
changelog/15191312504/10.4.19
changelog/15191547006/10.4.19
changelog/15191624225/10.4.19
changelog/15191735018/10.4.19
changelog/15192039615/10.4.19
changelog/15192345621/10.4.19
changelog/15192451633/10.4.19
changelog/15192578570/10.4.19
changelog/15192644336/10.4.19
changelog/15192738356/10.4.19
changelog/15192939938/10.4.19
changelog/15193271980/10.4.19
changelog/15193956539/10.4.19
changelog/15194127381/10.4.19
changelog/15194363892/10.4.19
changelog/15196895178/11.2.10
changelog/15197015526/11.3.7
changelog/15197016992/11.4.5
changelog/15197018727/11.5.5
changelog/15197020590/11.6.2
changelog/15197022768/12.0.1
changelog/15270800476/11.6.5
changelog/update-changelog-2025-06-17
charandas/add-org-role-to-id-token
charandas/allow-anonymous-without-allowAnonymous
charandas/custom-requestheader-auth-mt-authn
charandas/only-publish-metrics-for-remote-services
charandas/use-new-tracer-functionality
check-grafana-javascript-agent-enabled-faro
chore/betterer-github-actions
chore/bra-build-delay
chore/dashboards-app-sdk-0.39
chore/eslint-suppressions
chore/eslint-unused-directives
chore/fix-i18n-issues_apply-fixes
chore/fix-utils-i18n-import
chore/gen-apps
chore/groupsync-refactor-service-test-role-store
chore/label-internal-issues
chore/loki-editor-testing
chore/msw-improvemnts
chore/nested-folder-picker-overflow
chore/no-floating-promises-tests
chore/react-refresh
chore/refactor-groupsync-service-test
chore/skip-integration-tests
chore/swagger-display-operationids
chore/too-many-resources-to-sync
chore/update-governance
ci/parallellize-playwright-tests
cinaglia/tweak-ldap-warning-copy
clementduveau-patch-1
cli-add-kv-record-marking-migration-to-unified-storage-as-complete
cloud-alerting-info-card
code_scanning/placeholders
codegen/cleanup-core-schemas
codegen/codeowners-grafana-schema
codegen/cog-for-common
codegen/delete-cue.mod
codegen/migrate-ts-core-kinds
codeincarnate/image-cell-broken
codeincarnate/wrap-sort-fix
codeql-python-fix
colin-stuart/add-support-tickets-link-to-navtree
colin-stuart/id-token-add-display-name
collinfingar/editabletext/new-editable-text-component
collinfingar/grafana-ui/adding-unit-tests-2
collinfingar/querylibrary/public-private-toggle
color-refactor
connections-homepage
correct-audit-log-account-level-requirements
correlation-poc
create-diff
dana/add-secret-service-copy
dana/cloud-migrations/cloud-to-cloud-exclude
dana/cloud-migrations/fix-flake-get-snapshot-list
dana/cloud-migrations/flaky-test-get-snapshots
dana/cloud-migrations/grafana-version-metrics
dana/cloud-migrations/investigate-adding-version
dana/cloud-migrations/leave-flaky-test
dana/cloud-migrations/modify-snapshots-endpoint
dana/cloud-migrations/plugin-api-check
dana/cloud-migrations/plugin-migration-list-plugins
dana/cloud-migrations/plugin-migration-logos-trial
dana/cloud-migrations/plugin-migration-plugin-warning
dana/cloud-migrations/plugin-migration-safeguard
dana/cloud-migrations/test-migration-send
dana/cloud-migrations/use-resource-name-fe-josh-suggestion
dana/copy/cloud-migrations/plugin-migration
dana/ds-provisioning-caching
dana/ephemeral-inst/test-build
dana/ephemeral-inst/test-build-2
dana/ephemeral-inst/test-build-2105-b1b9
dana/ephemeral-instances/test-build-locally
dana/hackathon-checkboxes-fe
dana/provision-ds-query-caching
dana/secret-service/connect-FE-with-flow
dana/secret-service/connect-services-sql
dana/secret-service/default-gcm-cipher
dana/secret-service/filter-sv-by-status
dana/secret-service/implement-sql-keeper
dana/secret-service/keeper-configuration
dana/secret-service/michael-secret-keeper
dana/secret-service/rename-keeper-storage
dana/secret-service/start-spec
dana/secret-service/sv-method-for-decrypt
dana/secret-service/unify-keeper-types
dana/secret-service/wiring-initial
dana/secret-service/wiring-secret-keeper
dana/secret-service/wiring-secret-keeper-copy
danstadler-pdx-patch-1
dark-button-borders
darrenjaneczek/invisible-datasources
dash-schema-experiments-zod
dashboard-api-with-hub-version
dashboard-edit-variable-delete
dashboard-get-service
dashboard-keep-internal-id-on-create
dashboard-options-pane-item-unique
dashboard-permission-sql-update
dashboard-row-indentation
dashboard-scene-multil-layouts
dashboard-v1-v2-convert-annotations
dashboards-add-v1-status
dashboards-keep-descr-in-table
dashboards-service/feature-branch
datasource-description
db_statement
debounce-change-tracker
debug-bleve-memory-leakage
debug-log
delete_watcher
demo-prometheus-render-label-expr
dependabot/docker/alpine-3.22.0
dependabot/docker/alpine-3.22.1
dependabot/docker/golang-1.24.5-alpine
dependabot/docker/node-24-alpine
dependabot/github_actions/actions/setup-go-5.5.0
dependabot/github_actions/cypress-io/github-action-6.10.1
dependabot/github_actions/marocchino/sticky-pull-request-comment-2.9.4
dependabot/github_actions/peter-evans/create-pull-request-7.0.8
dependabot/github_actions/slackapi/slack-github-action-2.1.1
dependabot/go_modules/apps/advisor/golang.org/x/net-0.38.0
diegommm/new-migrator-package-based
diegommm/v11.2.x-chore-bump-pyroscope-go-godeltaprof
diegommm/v11.2.x-chore-bump-pyroscope-go-godeltaprof-2
diff-views
direct-local-server
disable-crowdin-forks
django
dmihai/ldap-docs-update
dmihai/scim-optimize-group-sync
dmihai/update-ldap-mod
dnd_link_actions
dockerfile-add-missing-dep
docs-1.x
docs-2.0
docs-2.1
docs-2.5
docs-2.6
docs-add-org-id-to-search-example
docs-rbac-action-definitions
docs-update-whatever-jasuade-test
docs/409-on-datasource-update
docs/add_branding_info_airgapped
docs/adding_api_login_rate_limit_info
docs/clarify_internal_grafana_metrics
docs/cortextool
docs/jvaldez-fixing-links
docs/simplified-exploration-add-missing-products-labels
docs/update-image-renderer-dependencies
docs/update-render-service-tracing
docs_v5.0
domas-refactor-nav-for-o11y-dept-phase-1-b
downstream-err-grpc
drclau/experiment-authz-interceptor
drclau/unistor/namespace_authorizer
drew08t/binary-operation-allow-alias
drew08t/canvas-developer-guide
drew08t/canvas-support-base64-image-src
drew08t/extend-all-numbers-to-unary
drew08t/geomap-dynamic-geojson-tooltip
drew08t/geomap-no-repeat-option
drew08t/pan-man-player-tracking
drew08t/state-timeline-state-filter
drew08t/table-ng-subtable
drew08t/table-react-data-grid
drew08t/table-react-table-8
drew08t/time-compare
drew08t/transformations-refid-exact-match
dropdown-shift-fix
ds-apiserver-with-configs
ds-ordering
ds-set-apiversion
dsApiVersion
dsuess/feat/dragndrop-dashboard-component
dw_mode3_fix
dw_mode_feature
e2e-selectors/dist-tag-modifications
e2e-selectors/version-poc
e2e-test-ap
e2e/panel-test-plugin
ed/custom-theme
edit-variables-poc
edpoole/command-palette-animations
edvard-expose-correlations
edvard/extend-trace-view-attribute-links
edvard/trace-view-attributes
edwardqian-label-suggestion-api
elastic-annotation-fix
eledobleefe/able-to-remove-options-multiselect-90900
eledobleefe/combobox-grouping-96093
eledobleefe/create-unified-history-feature-toggle-97865
eledobleefe/hackathon-tracking-events
eledobleefe/hackathon-tracking-events-v2
eledobleefe/history-docked-98953
eledobleefe/i18n-locale-backend-tests
eledobleefe/locale-dashboards-with-i18n-package-joshs-quick-poc
eledobleefe/locale-dashboards-with-i18n-package_TR
eledobleefe/multicombobox-grouping-96093
eledobleefe/query-320-256-66585
eledobleefe/unified-history-event-tracking-99822
eledobleefe/use-combobox-not-select-grafana-ui
eleijonmarck/actionsets/add-org-admin-to-folder-dashboard-creation
eleijonmarck/anon/ability-to-search-permissions
eleijonmarck/appptf-bugbash/shared-with-me-parent-folder
eleijonmarck/authz-service/memcached-client-refactor
eleijonmarck/authz-service/poc-basicroles
eleijonmarck/banner-service/add-update-verb
eleijonmarck/config/revert-editors-can-admin-change
eleijonmarck/dashboard-permissions/plugin-editor-role-update-fix
eleijonmarck/datasource-permissions/query-only-for-query-path
eleijonmarck/datasourcepermissions/add-additional-info-to-logs
eleijonmarck/fixes_broken_auth_groupsync_test
eleijonmarck/iam/script-to-launch-app
eleijonmarck/lbab-for-datasources/docs
eleijonmarck/lbac-data-sources/note-caching
eleijonmarck/lbac-for-datasources/add-teamuid-2
eleijonmarck/lbac-for-datasources/allow-serviceaccounts-passthrough
eleijonmarck/lbac-for-datasources/allowlist-for-datasources
eleijonmarck/lbac-for-datasources/allowlist-update-for-mimir
eleijonmarck/lbac-for-datasources/bug-fix
eleijonmarck/lbac-for-datasources/check-team-existance-before-adding-rule
eleijonmarck/lbac-for-datasources/enable-mimir
eleijonmarck/lbac-for-datasources/fix-for-serviceaccounts
eleijonmarck/lbac-for-datasources/ft-enable-mimir
eleijonmarck/lbac-for-datasources/handle-get-update-only-from-api
eleijonmarck/lbac-for-datasources/integration-tests
eleijonmarck/lbac-for-datasources/move-validation-to-lbac-rules
eleijonmarck/lbac-for-datasources/refactor
eleijonmarck/lbac-for-datasources/remove-sa-check-for-recommendations
eleijonmarck/lbac-rules/app-platform-poc-mode0
eleijonmarck/lbac-rules/deprecation
eleijonmarck/lbac-rules/pagination-of-rules
eleijonmarck/lbacfordatasources/search-filter
eleijonmarck/memcached-client/update-stale-serverlist
eleijonmarck/memcached-client/updatedintervalandconnectionchecks
eleijonmarck/memcached/updateinternal-to-30-seconds
eleijonmarck/mp3o/no-access-to-parent
eleijonmarck/plugin-rbac/add-ability-for-multiple-actions-in-reqActions
eleijonmarck/recorded-query-user/query-datasource-permissions
eleijonmarck/remove-setting/viewers_can_edit
eleijonmarck/search-listings
eleijonmarck/subfolder-creation/actionset-enabled
eleijonmarck/teamlbac/ux-mitch-improvements
eleijonmarck/zanzana/run-migration-as-openfga
elliot/add-share-url-button
em/hackathon/wingman-anomalies-sorting-upgrades
embeddable-dash
emil/202212/errata
enrichi
eq-dashgpt-debug
etcd-storage-backend
ethirolle-patch-1
evictorero/add-tracing-image-renderer
evictorero/short-url-app-platform
evictorero/snapshots-config-disable-external
explore-compact-mode
explore/fonster-mgr
exploremetrics/unit/recordingrulesparsing
extensions/e2e-test-added-components
extensions/logs
extensions/refactor-added-links-drone-test
extensions/refactor-registry
extensions/use-new-links-hook-in-core_alerting
fast
fastfrwrd/fix-table-rename-targetting
fastfrwrd/fix-tooltip-ellipsis
fastfrwrd/ignore-enterprise-source-files-prettier
fastfrwrd/pills-colors-increasing
fastfrwrd/pills-math-increases
fastfrwrd/tableng-final-style-tweaks
fastfrwrd/tableng-footer-rebased
fastfrwrd/tableng-markdown-cell
fastfrwrd/tableng-rendercell
fastfrwrd/tableng-sparkline-minmax
fastfrwrd/tableng-style-tweaks-minus-row-height
fastfrwrd/tableng-wrap-headers-dial-in-widths
fe-ops/jest-swc
feat-move-team-picker-to-runtime
feat-new-ds-picker-to-runtime
feat/allow_modal_to_render_under_plugin
feat/frontend-accesscontrol-authorizer
feat/group-attr-sync-ui
feat/groupsync-user-assignment-ux
feat/healthcheck-2-gmd
feat/iam-user-identity-int-id-check
feat/nodegraph-custom-fields
feat/shadow-search-traffic
feature/add-submissions-endpoints
feature/git-sync-pure-git
femt/fonts-path
femt/img-build-paths_backend
field_config_one_click_datalinks
file-read-info
filewalkwithme/unistore-modify-guardian-to-search-folders-via-folder-service
filewalkwithme/unistore-new-endpoint-sample
fix-TestIntegrationFoldersGetAPIEndpointK8S
fix-add-dash-folder-support
fix-annotations-mode-3
fix-api-validation-list-mode0
fix-auto-grid-panel-editing
fix-broken-link
fix-depedencies-unified-storage
fix-filename
fix-flaky-watch-test
fix-folder-pagination
fix-issue-with-authz
fix-metrics-storage
fix-padding-options-pane
fix-preserve-url-state-alt-fix
fix-preserver-url-hihide-options
fix-repoinfo-on-dual-writers
fix-sharedwithme-folders-unistore
fix-swagger-gen
fix-tabbedcontent-expand
fix-table-ng-scrollbar
fix-template-example
fix-vendoring-issues
fix-vendoring-issues-2
fix/92181
fix/92260
fix/app-runner-tracing
fix/dashboard-migration-missing-versions
fix/drilldown-app-feature-toggles
fix/use-home-page-on-dashboard-not-found
focus-style-update
folder-list-limit-bump
folder-remove-canAdmin
folder-replace-authz-client
folder-service-cache
folder-tracing
folder/admission_hook
folder/library_element_folder_table
folder/max_depth
folder_delete_validate
folders-fix-dependency-on-dash-store
folders/e2e_tests
frontend-notification-system
gabor/bump-grafana-experimental
gabor/esc-core
gabor/fix-toggle-test
gabor/refactor-client
gabor/v11-2-x-yarn-resolution-fix
gamab/apis-proxy/authn
gamab/authz/allow-insecure
gamab/authz/app-2
gamab/authz/better-query
gamab/authz/cache-trace-1
gamab/authz/cloud-mode
gamab/authz/id-scope-res
gamab/authz/provide-to-new
gamab/authz/roles
gamab/authz/skeleton
gamab/ff/switch-authz-client
gamab/oncall/plugin-rename
gamab/plugins/include-access-action
gamab/plugins/use-permreg
gareth/jaeger-feature-toggle-default
gareth/remove-jaeger-ft
gc/14844676959
gen/custom-templates
git-export-with-history
git-provisioing-legacy-export
git-sync-use-secrets-service
git-ui-sync/fix-resource-message
git-ui-sync/status-polling
github-pr-from-frontend
giuseppe/feature-toggles-env-vars
giuseppe/hg-install-token-cli
giuseppe/loader-refactoring-ctx
giuseppe/plugins-cdn-metrics
giuseppe/plugins-sri-backend-follow-up
gloom-theme-blue
grafakus/remove-metricssummary-feature-toggle
grafana-docs-image
grafana-grafana-next-robbymilo/relref-replace-grafana-next
grafana-grafana-v11.5-robbymilo/whats-new-move
grafana-ui/collapsible-section-color
grafana/grafana-next-robbymilo/test-reversal-tool-2
grafana_indexer_poc
grafanal-flamegraph-license
grafsean/docs-openapi-example-1
grafuzer-patch-1
grambbledook/grafana-com-nightly-gha
grambbledook/grafana-main-notify
grambbledook/inegration-tests-gha
grambbledook/move-cloudwatch-config-to-binary
grambbledook/remove-ignore-path
grambbledook/test-seq-changelog-no-wb
grambbledook/test-seq-changelog-wb
grambbledook/test-seq-pr
grambbledook/test-sequential-cl
graph_bar_gauge_migration
gtk-grafana/drawer/z-index-restore-focus-props
gtk-grafana/issues/105022/logs-table-not-rendering__newLogsPanel
gtk-grafana/logs-drilldown-rename
gtk-grafana/logs/logs-panel-memory-leak-investigation
gtk-grafana/logs/logs-table-ui/body-line-wrap
gtk-grafana/logsPanelControls/enable-by-default
gtk-grafana/query-sharding-hack-day
gtk-grafana/support-escalations/issues/12151/shared-tooltip-not-clearing
gtk-grafana/ui-feedback__buttons
gtk-grafana/ui-feedback__buttons__toggle-icon
gtk-grafana/ui-feedback__buttons__toolbar-icon
gtk-grafana/ui-feedback__buttons__toolbar-icons
guarantee_no_rv
guarantee_uid_write
hackathon-12-dash
hackathon-12/track-attack
hackathon-13-grafanaql
hackathon-13-grafanaql-api-server
hackathon-13-stego
hackathon-13/git-sync/more-llm-friendly-endpoints
hackathon-13/git-sync/refs-endpoint
hackathon-13/grafanaql/investigations
hackathon-13/grafanaql/register-playlist-app
hackathon-13/grafanaql/scaffolding
hackathon-2024-08/grafana-cloud-notifications
hackathon-2024-08/mermaid
hackathon-command-line
hackathon-p2g
hackathon-tracking-events-no-ast
hackathon/domas-trace-flame-chart-view
hackathon/grot9000
hackathon/i18n-all-the-things
hackathon/improve_span_detail
hackathon/insta-dash
hackathon/miso-traceable
hackathon/p2g
hackathon/report-issue-button-copy
hackathon12-folders-searchapi
hackathon12/folders
hackathon12/folders-leonor
hackathon_repair_service
hackaton-13/upgrade-your-upgrade
hackaton/boostrap-feedback-app-sdk
hackaton/report-issue-button
hackaton/user-cache-test
hackatthon12/folders-leonor
hairyhenderson/drone-remove-unused-image-refs
hairyhenderson/enable-faro-tracing
hairyhenderson/index-handler-test
hairyhenderson/lint-reenable-gocritic
hairyhenderson/lint-with-goimports
haris/dash-schema-experiments/alerts-annotations
haris/dash-schema/panel-id-expm
haris/dash-schema/resp-trans-v1
haris/dash-schemav2/uid-and-version
haris/explore/fonster-mgr/drag-and-drop
haris/explore/query-editor-bug
haris/migrate-to-v28
haris/query-library/enhance-user-data
haris/query-library/enhance-user-data-3
haris/schemav2-refactor-vizconfigkind
hide-disable-for-provisioned-plugins
hugoh/barrel-files-III
hugoh/expose-i18n-in-runtime
hugoh/fix-error-handling-in-backendSrv
hugoh/use-grafana-i18n-in-grafana-ui
hugoh/use-i18n-in-grafana-ui
hugoh/wrongly-placed-usetranslate
i18n/followup-rule-tweaks
i18n/package-update-imports
iam/model-rbac
iam/server-admin-elevate-org-privileges
identity/remove-typed-id
ieva/add-user-uid-to-user-role
ieva/change-default-folder-dash-perms
ieva/fix-permissin-validation
ieva/perm-validation-for-group-attr-sync
ieva/remove-authzgrpcservice-toggle
ieva/sunset-groupsync-pt1
ifrost/add-scroll-container-to-explore
ifrost/app-links-poc
ifrost/aw-snap
ifrost/fix-loki-resize
ifrost/just-testing
ifrost/links-to-explore-apps
ifrost/make-pyroscope-annotations-optional
ifrost/saved-views
ifrost/tempo-streaming-branch/patch
ifrost/toString-label
ifrost/toolbar-button-size
ihm/040724-add-alt-text-v7.0
ihm/040724-add-alt-text-v7.2
ihm/040724-add-alt-text-v7.5
ihm/040724-add-alt-text-v8.0
ihm/040724-fix-alt-text-heatmap
ihm/05/03/25-fix-broken-links
ihm/070325-query-library-v5
ihm/230824-canvas-actions-updates
ihm/250527-update-feature-flag-info
ihm/250618-fix-table-cell-types
ihm/250708-variables-structure-concepts-improvement
ihm/250709-geomap-tooltip-clarification
imarkvisser/main
img-src-blob
improve-provisioning-tests
include-managed-by-for-dashboards
index-internal-id
inf0rmer/remove-nested-folders-feature-toggle
instant
iortega/dash-schema-experiments/ts-to-openapi
iortega/new-ds-model-backup
iortega/parse-boolean-fully-in-url
iortega/run-old-arch-e2e-tests-locally
irenerl24-patch-2
irenerl24-patch-3
irl/schemav2
ismail/2-new-lang-provider-methods
ismail/4-support-series-api-from-start
ismail/7-use-new-methods-in-variable-editor
ismail/auto-completion-after-three-letters
ismail/fallback-to-series-endpoint
ismail/prom-on-app-platform
ismail/remove-deprecated-language-provider-methods
ismail/remove-get-calls
ismail/remove-prometheusCodeModeMetricNamesSearch
ismail/update-resource-call-flow
issue-13623
ivana/loki-remove-lokiLabelNamesQueryApi
iwysiu/94184
jackandhugo/e2e-provisioning-app
jackhugo/levitate-fix
jackw/better-filter-barrel-files
jackw/betterer-node24
jackw/direct-lodash-imports
jackw/fe-caches-dir
jackw/fix-e2e-plugin-configs
jackw/lazy-load-fe-sandbox
jackw/poc-rspack
jackw/poc-rspack-decoupled
jackw/poc-vite
jackw/remove-core-actions-barrel-file
jackw/remove-dashboardplugin-barrel
jackw/replace-lerna-with-nx
jackw/rolldown
jackw/rspack-plugins
jacobsonmt/contact-export-snapshot-test
jacobsonmt/contact-export-snapshots
jacobsonmt/fix-missing-receiver-fields
jacobsonmt/hackathon202506/multipleroutes
jacobsonmt/oauth2-other-http-notifiers
jacobsonmt/receiver-auth-hook-up
jalevin/bench_tests_frontend
janthoe/app-platform-settings-prototype
javi/add_new_gray_variant_to_badge
jcalisto/fix-apis-concurrent-queries
jdb/2024-08-explore-reorganization-v11.2
jdb/2024-08-revert-scenes-things-no-89573
jdb/2024-09-generate-whats-new-entry
jdb/2024-09-link-to-row
jdb/2025-05/add-docs-license
jdbaldry-patch-1
jesdavpet/106028-fix-canvas-connection-point-z-index-css-only
jgs/add-adaptiveprofiles-nav
jh/a11y-workflow-improvement
jh/backport-action
jh/build-plugins-into-build-dir
jh/contexthandler-middleware-spans
jh/default-target-config
jh/fe-service-docker-image-cross-os
jh/fix-measureText-for-tnums
jh/fs-http-middleware
jh/fs-redirect-to-login
jh/fs-unavail-backend
jh/go-mod-stuff
jh/login-api-route
jh/new-rudderstack-sdk
jh/playwright-gha
jh/preference-debug-logging
jh/pw-gha
jh/quickRanges-fix
jh/remove-old-images
jh/share-yarn
jh/test-commit-signing
jh/test-log-fetch-polyfills
joannaWebDev/feat-PoC-customizable-tooltip
joannaWebDev/improve-a11y-switch
joeb/49371/alert-state-state-rename
joey/gracefully-handle-range-error
joey/tags-time-range
joey/trace-view-skipHeader
joshhunt/97577-prom-combobox-label-filter-item
joshhunt/ash/grafana-sql-i18n-debugging
joshhunt/better-gen-toggles
joshhunt/combobox-use-options
joshhunt/debug-backport-action
joshhunt/fix-schemav2-typescript
joshhunt/gutting-the-dom
joshhunt/library-panel-page-folder-filter
joshhunt/new-command-palette
joshhunt/no-backdrop-blur-toggle-default-enabled
joshhunt/organise-stories
joshhunt/poc-custom-value-component
joshhunt/poc-move-frontend-into-a-folder
joshhunt/rudderstack-menu-docked-state
joshhunt/runtime-components-docs
joshhunt/simpler-use-options-fn
joshhunt/slightly-better-async
joshhunt/spike-new-new-browse-dashboards
joshhunt/test-new-gpg-key
joshhunt/trash-actions
josmperez/e2e-style
juanicabanas/public-dashboard-naming
juanicabanas/public-dashboard-panels-fix
juanicabanas/reporting-template-variables-test
juanicabanas/share-view-qp-redesign-array
juanicabanas/whole-reporting
julienduchesne/annotations-api-dashboard-uid
julienduchesne/nullable-date
justinrandell/cue-gen-errors
justinrandell/ds-apiserver-with-configs
k-bar-styles
k8s-add-v1-validation
k8s-dash-list-update-rvs
k8s-dashboard-v2-stub-in-legacy
k8s-dashboard-v2-stub-in-sql
k8s-dashboards-ga
k8s-fix-search-limit-dashboards
k8s-identity-api-server-fix-mysql-quotes
k8s-increase-search-limit
k8s-make-dashboards-available-in-cloud
k8sclient-featureflag-tests
kat/exm-homepage-fast-nick
kat/exm-homepage-torkel
kb/exprDSQueryApiIssue106560
kb/makeInfoSchemaWorkNoMerge
kb/moreSQLExprMetricWork
kb/sqlExprMultiTSFix
kb/sqlExprTime
kb/sqlExprTimeFuncs
kevinwcyu/fix-reading-auth-settings
kevinwcyu/make-alert-expr-grouping-opt-in
kevinwcyu/show-alert-rules-for-amazon-prometheus
km/move-rrc-to-gha
km/unshallow-on-release-build
konrad-pagination-branch
konrad-poc/alerting-insights
konrad-poc/alerting-loader-worker
konrad-poc/grafana-rules-api
kristina/DO-NOT-MERGE-ephemeral
kristina/add-edit-mode
kristina/add-frame-name
kristina/asdf
kristina/corr-dash-scenes
kristina/correlation-migrate
kristina/correlations-docs-external
kristina/correlations-external
kristina/correlations-in-dashboards
kristina/correlations-logs-labels
kristina/correlations_tutorial
kristina/count-bug-backport-11.6
kristina/dnd_link_actions
kristina/filter-select-all-none
kristina/filter-variables
kristina/gauge-sort
kristina/graph-bkgd
kristina/graph-bkgd-2
kristina/keep-contents-group-by
kristina/log-scale-trend
kristina/matrix-extract-bug
kristina/ms-in-db
kristina/override-short-in-explore
kristina/pre_correlations-in-dashboards
kristina/prep-time-series-long
kristina/query-library-user-data
kristina/remove-compact-dep-msg
kristina/sql-exp-autocomplete
kristina/state-timeline-etc
kristina/table-frame-list
kristina/variable-interp
kristina/variables-value-mappings
kubectl-dataquery-issue
kvstore
kvstore-17
kvstore-6
laura/feat/add-documentation-for-restoredashboards-feature
laura/feat/create-folder-functionality-in-folderpicker
layout/body-scroll-container
layouts-refactor
ldeveikis/migrate_dek_xorm
ldeveikis/ommit_finalized_xorm
ldeveikis/remove_secrets_nullable_db
leeoniya/11.2-webpack-bundle-analyzer
leeoniya/beforefore
leeoniya/codemirror
leeoniya/data-macro-frames
leeoniya/displayName-recalc
leeoniya/field-actions-one-click
leeoniya/graphng-hideFrom-plotLegend
leeoniya/graveyard-dig
leeoniya/improve-tableng-types
leeoniya/measure-before
leeoniya/measure-lcp
leeoniya/native-heatmap-zero-bounds
leeoniya/nownow
leeoniya/remove-deprecated
leeoniya/select-profile-play
leeoniya/select-profile-play2
leeoniya/state-timeline-fix-dual-time-multi-series
leeoniya/state-timeline-hidden-links
leeoniya/state-timeline-value-mappings
leeoniya/tableng-autocell
leeoniya/tableng-back-to-basics-og
leeoniya/timeseries-exemplars-rewrite
leeoniya/timeseries-sparse-points-nulls-fix
leeoniya/tooltips-respect-hideFrom
leeoniya/vizactions-more-methods
leeoniya/xy-chart-relax-color-size
leeoniya/xychart-remove-old
legacy-storage-getter
leventebalogh/extensions-logs-warning
leventebalogh/extensions-racing-condition-fix
leventebalogh/extensions/refactor-exported-components
leventebalogh/fix-confirm-modal
leventebalogh/poc-exposing-restricted-apis
leventebalogh/sidecar-idea-1
levitate-pipeline-test
lib-panel-escape
lib-panel-repeats-move
lib-panels-fix-view-panel
lib-panels-repeat-mig
library_element/get_all
library_element/get_without_dashboard
link-from-trace-to-explore-profiles
linoman/add_ldap_drawer
linoman/docs-add_pingidentity
linoman/saml_update_access_token_url
linoman/scim-poc
linoman/sso_ldap_add_ui_tests
lockfreerv
log-streaming
log_mod
logs-main
loki-query-sharding
loki_hook_up_scopes_rewrite
lucychen/sharingredesign_add_tests
lucychen/test_ir_3.12.2
macabu/ac-test-secrets
macabu/add-mockery-to-tools
macabu/alternative-sqlite-impl
macabu/bra-only-build-backend-inc-delay-ignore-test
macabu/build-pkg-aws-v2
macabu/conditionally-migrate-resources
macabu/e2c-bulk-insert-fix-slices-chunk
macabu/fix-gomod-enterprise-drift
macabu/gms-warn-contact-points-without-integratio
macabu/go-modernize
macabu/int-tests-org-name
macabu/keeper-only-delete-leaf
macabu/poc-snapshot-builder
macabu/refactor-decrypt-authz-flow
macabu/replace-jsoniter-simple
macabu/scopes-reenable-loki-query-inject
macabu/secret-audit-log-poc
macabu/secret-svc-draft-design-poc
macabu/secrets-add-authz-client
macabu/secrets-add-typed-client-1
macabu/secrets-add-typed-client-2
macabu/secrets-client-add-authz-checks
macabu/secrets-client-map-error-to-k8s
macabu/secrets-create-return-202
macabu/secrets-decrypt-authz-svc-identity
macabu/secrets-keep-ref-2
macabu/secrets-list-refactor-test1
macabu/secrets-store-api-version-db
macabu/secrets-v1beta1
macabu/secrets-v1beta1-spec
macabu/secrets-v1beta1-with-cue-and-common-securevalue
macabu/sql-migrator-with-sqlx
macabu/subresource-decrypt-poc
macabu/sync-from-main-release-10.4.19
macabu/sync-from-main-release-11.2.10
macabu/sync-from-main-release-11.3.7
macabu/sync-from-main-release-11.4.5
macabu/sync-from-main-release-11.5.5
macabu/sync-from-main-release-11.6.2
macabu/test-access-policy-token-dashboard-create
macabu/test-add-newline-to-printf
macabu/test-go-bench-executor-test
macabu/test-returning-method-driver
macabu/test-secrets-k8s
macabu/update-go-1-24-5
macabu/use-new-init-authz-client
macabu/use-std-crypto
main
make-feature-toggles-api-namespaced
marcoabreu/app-platform-wg-265/schema-validation-backup
marcoabreu/app-platform-wg-265/schema-validation-schema-changes
marcoabreu/dashboard-cleanup-id-check
margotphelps-patch-1
margotphelps-patch-2
mariell/backport-gha-11.3.9
mariell/biome
mariell/comrak
mariell/folder-titles-as-name
mariell/gocacheprog
mariell/gs/enforce-folder-rules
mariell/gs/git
mariell/gs/sanity-check-fixing-tree
mariell/new-sqlstore-test-infra
mariell/poc/working-setup
mariell/prototyping/pretend-oauth-api
mariell/remove-testsuite
mariell/time-integration-tests
master
matryer-docs-explore-links
matryer/wider
matyax/datasource-label-types-2
matyax/dynamic-time-splitting
matyax/faster-dedup
matyax/ga-shard-splitting
matyax/grafana-hoverbot
matyax/grafana-hoverbot-deployable
matyax/hackathon-2024-streamers
matyax/infinte-scroll-bottom-edge
matyax/interpolate-infinite-scrolling
matyax/log-row-less-recalcs
matyax/logs-order-direction
matyax/logs-panel-details-mode
matyax/logs-panel-v2-new-viz-details
matyax/logs-panel-v2-new-viz-details-2
matyax/logs-panel-v2-new-viz-feedback
matyax/logs-panel-v2-new-viz-highlighting
matyax/logs-panel-v2-new-viz-infinite-scroll
matyax/logs-panel-v2-new-viz-log-details
matyax/logs-panel-v2-new-viz-multi-details
matyax/loki-sort-direction
matyax/merge-responses-peformance
matyax/otel-logs-poc
matyax/query-splitting-with-sharding
matyax/shard-splitting
matyax/sharded-metric-queries
matyax/virtualized-log-rows
matyax/virtualized-log-rows-2
mckn/extensions-issue-recreate
mckn/extensions-logging
mckn/extensions-logging-2-LV-tests
mckn/poc-explore-links
mckn/trying-to-find-error
mdvictor/allow-injected-filters-edit
mdvictor/always-preserve-url-state
mdvictor/applicability-refactor
mdvictor/fix-group-by-sticky
mdvictor/fix-scopes-var-scenes
mdvictor/get-suggestions-ignore-label-name-in-scope
mdvictor/injected-filters-edit
mdvictor/manual-revert-scopes-filters
mdvictor/only-restore-url-state-on-dash-change
mdvictor/preserve-dash-params-navigation
mdvictor/reload-behaviour-no-timeout
mdvictor/scopes-filters-e2es
mdvictor/test-scopes-fix
mdvictor/test-scopes-fix-title
merge_scope_filters_into_or
metrics-drilldown-docs
metrics-explore-scenes-react
metrics_storage
mgyongyosi/def-cue-for-resources
mgyongyosi/poc-user-external-session-handling
mgyongyosi/resource-def-users-service-acc
mhamid/rbac-jwt-roles
migrate-correlations-workshop
migrateQueryBackend
migrateQueryFrontend
migration-assistant/include-alerts-in-snapshot
mihai/dual-write-team-members
mihai/fix-readme
mihai/hackathon
minisearch
miscellanous-improvements
miso-traceable
mja/hackathon-enrichment
mmandrus/go-client
mmandrus/store-snapshot-in-db
mmandrus/unified-kms-defunct
mmandrus/update-readme
mmandrus/use-KMS-in-MT
mob/dashboard-migrator
monodot-teamlbac-update
moose-docs-update-1
moustafab/alerting-pagination-folders-groups
moustafab/alpha-rule-api
moustafab/fix-update-swagger
moustafab/hackathon-2024-12-alerting-oncall-simplified
move-indexer-to-search-package
move-infra-logs-module
move-logs-tracing-to-module
move-provisioning-samples-to-devenv
move-quick-add-to-megamenu
mrdlesniak-patch-1
mssql-overhaul-052025
natellium-update-transformations
nav/ml-access-fix
nav/pin-items
new-app-workshop
njvrzm/cloudwatch-nil-pointer-guard
njvrzm/cloudwatch-v2-backport-11.4.7-frankenstein
njvrzm/test-release-12.0.3-ci
njvrzm/update-cloudwatch-temp-credentials-docs
no-clone-keys
non-working-nested-field-overrides
nwrichmond/decouple-implementation-details-from-related-logs-scene
nwrichmond/functional-flavor-decouple-implementation-details-from-related-logs-scene
ofrep-builder
only-edit-pane
opex/hackathon-13/frontend
opex/hackathon-13/upgrade-challenges
opex/hackaton-13/manual-api-builder
opex/secret-service-poc
organize-behaviors
origin/kb/sqlExprAlerting
oscark/Add-now-parameter-to-parse-function
oscark/bump-scenes-5.21.2
oscark/copy-rows-tabs
oscark/keyboard-shortcut-copy-paste
oscark/library-panels-should-have-the-same-hooverHeader-behavior-as-normal-panels
oscark/make-rows-easier-to-select
oscark/rename-responsive-grid-files
oscark/simplify-DashboardGridItem-repeat
overwrite-param-example-doc-update
page-canvas
pan-man
panel-chrome-selection
panel-edit-edit-source
panel-edit-options-refactor
panel-search-behavior
panel-search-use-context
papagian/app-platform-settings-prototype
papagian/config-provider
papagian/dash-delete-add-missing-index
papagian/release-11.2.10
papagian/search-rec-query
papagian/search-starred
patch-2
patch-3
pepe/alerting-docs-alerting-rule-group-rules-option
pepe/alerting-docs-differentiate-template-name-and-title
pepe/alerting-docs-time-range-in-alert-view-page
pepe/alerting-docs-tutorials
pepe/alerting-ui-template-name-input
pepe/service-account-ref-links
perf-benchmark
pin-header
pkg/apis_module
playlists-workshop
plugin-assetpath-refactor
plugin-dependency-install
plugin-settings-apiserver
plugincdn-install-test
plugins-express
pluginstore-run
pmarbach/tableng-max-wrap-lines
poc-interface-dashboard-manager
poc-prom-app
poc/enrichment-tree
poc_type_aliases
postMigrateQueryDataExample
postgres-host-handling
postgres/config-redesign-1
postgres/diagnostics-docs-update
postgres/remove-postgresVersion
preferences-app
prepare-update-ts
preserve-dash-params-navigation
promMultipleEqual
promSuggestGroupBy
prometheus/bohandley-add-limit-for-client-calls-for-metric-names
prototype/hover-using-css
provisionign-rename
provisioning-add-frontent-stubs
provisioning-apiserver
provisioning-avoid-zero-date
provisioning-client
provisioning-renderer
provisioning-support-nested-paths
provisioning-update-status
provisioning-validation
provisioning-with-featToggle
provisioning/add-providers
provisioning/field-errors
provisioning/job-errors
provisioning/skip-sync
public-dashboards-fix-last-reference
public-dashboards-remove-folder-ref
qos-unified-storage
querier-return-fast
query-group/functional-component
query-library/move-api
query-options-messages
query-resolution
raw-data-us
react-calendar-patch
reduce_github_pr_template
refactor-dwm1
refactor/package-structure-around-webhook
refresh-input-chore
reintroduce-permissions-index-by-role-action-scope
release-0.0.0-cloud.0
release-10.0.0
release-10.0.1
release-10.0.10
release-10.0.11
release-10.0.12
release-10.0.13
release-10.0.2
release-10.0.3
release-10.0.4
release-10.0.5
release-10.0.6
release-10.0.8
release-10.0.9
release-10.1.0
release-10.1.1
release-10.1.10
release-10.1.2
release-10.1.4
release-10.1.5
release-10.1.6
release-10.1.7
release-10.1.8
release-10.1.9
release-10.2.0
release-10.2.1
release-10.2.2
release-10.2.3
release-10.2.4
release-10.2.5
release-10.2.6
release-10.2.7
release-10.2.8
release-10.2.9
release-10.2.91
release-10.3.0
release-10.3.1
release-10.3.10
release-10.3.11
release-10.3.12
release-10.3.3
release-10.3.4
release-10.3.5
release-10.3.6
release-10.3.7
release-10.3.8
release-10.3.9
release-10.4.0
release-10.4.1
release-10.4.10
release-10.4.11
release-10.4.12
release-10.4.13
release-10.4.14
release-10.4.15
release-10.4.16
release-10.4.17
release-10.4.17+security-01
release-10.4.18
release-10.4.18+security-01
release-10.4.19
release-10.4.19+security-01
release-10.4.2
release-10.4.20
release-10.4.3
release-10.4.4
release-10.4.5
release-10.4.6
release-10.4.7
release-10.4.8
release-10.4.9
release-11.0.0
release-11.0.0-preview
release-11.0.1
release-11.0.10
release-11.0.11
release-11.0.12
release-11.0.2
release-11.0.3
release-11.0.4
release-11.0.5
release-11.0.5+security-01
release-11.0.6
release-11.0.6+security-01
release-11.0.7
release-11.0.8
release-11.0.9
release-11.1.0
release-11.1.1
release-11.1.10
release-11.1.11
release-11.1.12
release-11.1.13
release-11.1.14
release-11.1.2
release-11.1.3
release-11.1.4
release-11.1.5
release-11.1.6
release-11.1.6+security-01
release-11.1.7
release-11.1.7+security-01
release-11.1.8
release-11.1.9
release-11.2.0
release-11.2.1
release-11.2.1+security-01
release-11.2.10
release-11.2.10+security-01
release-11.2.11
release-11.2.2
release-11.2.2+security-01
release-11.2.3
release-11.2.3+security-01
release-11.2.4
release-11.2.5
release-11.2.6
release-11.2.7
release-11.2.8
release-11.2.8+security-01
release-11.2.9
release-11.2.9+security-01
release-11.3.0
release-11.3.0+security-01
release-11.3.1
release-11.3.2
release-11.3.3
release-11.3.4
release-11.3.5
release-11.3.5+security-01
release-11.3.6
release-11.3.6+security-01
release-11.3.7
release-11.3.7+security-01
release-11.3.8
release-11.3.8+security-01
release-11.3.9
release-11.4.0
release-11.4.1
release-11.4.2
release-11.4.3
release-11.4.3+security-01
release-11.4.4
release-11.4.4+security-01
release-11.4.5
release-11.4.5+security-01
release-11.4.6
release-11.4.6+security-01
release-11.4.7
release-11.5.0
release-11.5.1
release-11.5.2
release-11.5.3
release-11.5.3+security-01
release-11.5.4
release-11.5.4+security-01
release-11.5.5
release-11.5.5+security-01
release-11.5.6
release-11.5.6+security-01
release-11.5.7
release-11.6.0
release-11.6.0+security-01
release-11.6.0-Update-JWT-library-CVE-2025-30204
release-11.6.1
release-11.6.1+security-01
release-11.6.2
release-11.6.2+security-01
release-11.6.3
release-11.6.3+security-01
release-11.6.4
release-12-0-1-ds-type-lookup
release-12-0-1-ds-type-lookup-2
release-12-0-ds-type-lookup
release-12.0.0
release-12.0.0+security-01
release-12.0.1
release-12.0.1+security-01
release-12.0.1-backport-pr-104605
release-12.0.2
release-12.0.2+security-01
release-12.0.3
release-12.1.0
release-8-2-3
release-8.3.10
release-8.3.11
release-8.3.7
release-8.4.0
release-8.4.10
release-8.4.11
release-8.4.2
release-8.4.3
release-8.4.4
release-8.4.5
release-8.4.6
release-8.4.7
release-8.5.0
release-8.5.0-beta1
release-8.5.1
release-8.5.10
release-8.5.11
release-8.5.13
release-8.5.14
release-8.5.15
release-8.5.2
release-8.5.20
release-8.5.21
release-8.5.22
release-8.5.24
release-8.5.26
release-8.5.27
release-8.5.3
release-8.5.4
release-8.5.5
release-8.5.6
release-8.5.9
release-8.5.9-take2
release-823
release-9.0.0-beta1
release-9.0.0-beta2
release-9.0.0-beta3
release-9.0.1
release-9.0.2
release-9.0.3
release-9.0.4
release-9.0.5
release-9.0.6
release-9.0.7
release-9.0.8
release-9.0.9
release-9.1.0
release-9.1.0-beta1
release-9.1.1
release-9.1.2
release-9.1.3
release-9.1.4
release-9.1.5
release-9.1.6
release-9.1.7
release-9.1.8
release-9.2.0
release-9.2.0-beta1
release-9.2.1
release-9.2.10
release-9.2.13
release-9.2.15
release-9.2.17
release-9.2.18
release-9.2.19
release-9.2.2
release-9.2.20
release-9.2.3
release-9.2.4
release-9.2.5
release-9.2.6
release-9.2.7
release-9.2.8
release-9.3.0
release-9.3.0-beta1
release-9.3.11
release-9.3.13
release-9.3.14
release-9.3.15
release-9.3.16
release-9.3.2
release-9.3.4
release-9.3.6
release-9.3.8
release-9.4.0-beta1
release-9.4.0-public
release-9.4.1
release-9.4.10
release-9.4.12
release-9.4.13
release-9.4.14
release-9.4.15
release-9.4.17
release-9.4.2
release-9.4.3
release-9.4.7
release-9.4.9
release-9.5.0
release-9.5.1
release-9.5.10
release-9.5.12
release-9.5.13
release-9.5.14
release-9.5.15
release-9.5.16
release-9.5.17
release-9.5.18
release-9.5.19
release-9.5.2
release-9.5.20
release-9.5.21
release-9.5.3
release-9.5.5
release-9.5.6
release-9.5.7
release-9.5.8
release-9.5.9
release-v9.0.0
release/10100684153/11.1.1
release/10101103482/11.1.1
release/10101187064/11.1.1
release/10102650044/10.2.9
release/10118284765/11.1.3
release/10581619470/11.2.0
release/10581841523/11.2.0
release/11382147019/11.0.5+security-01
release/11382582831/11.0.5+security-01
release/11384984776/11.0.5+security-01
release/11385224277/11.0.5+security-01
release/11385297718/11.0.5+security-01
release/11385710935/11.0.5+security-01
release/11385963777/11.0.5+security-01
release/11386309680/11.0.5+security-01
release/11386417537/11.0.5+security-01
release/11390255380/11.2.2+security-01
release/11391162998/11.1.7+security-01
release/11465115178/11.3.0
release/11798304752/11.3.0+security-01
release/11799132767/11.3.0+security-01
release/11799291799/11.3.0+security-01
release/12167153824/11.3.2
release/13400427896/11.3.4
release/13400795059/11.3.4
release/13401021557/11.3.4
release/14602297676/11.4.3+security-01
release/14602764065/11.5.3+security-01
release/231/10.4.19
release/233/10.4.19
release/236/10.4.19
release/255/11.2.10+security-01
release/269/12.0.2
reload-behaviour-refactor-typecheck
remove-angular
remove-dashboards-folders-cli-ff
remove-dbProviderFunc
remove-deprecated-dashboard-api
remove-deprecated-folder-api
remove-deprecated-stars-api
remove-grpc-feature-flag
remove-search-ff
remove_grpcutils
renovate/braintree-sanitize-url-7.x
renovate/grafana-eslint-config-8.x
renovate/grafana-plugin-e2e-2.x
renovate/kusto-monaco-kusto-13.x
renovate/locker
renovate/moment-timezone-0.x
renovate/ol-10.x
renovate/react-data-grid-digest
renovate/react-router-monorepo
renovate/tanstack-virtual-monorepo
repeat-url-sync
repeat-url-sync2
replicator-reuse-parser
repo-cleanup
repo-on-legacy-folder
reporting-apps-hackathon-project
require-meta
resource-add-title-and-id
resource-server-history
resource-server-watch-test
resource-storage-with-tests
resource-store
resource-store-indexing
resource-store-watch-tests
revert-100018-backport-99998-to-v11.5.x
revert-102036-jackw/grafana-data-internal
revert-103961-zoltan/pgx
revert-106596-moustafab/add-provenance-to-prom-api
revert-7bca698
revert-88664-santihernandezc/make_remote_alertmanager_integration_tests_non_blocking
revert-91888-dashboard-scene-body-scrolling
revert-94118-ihm/011024-sharing-aliases
revert-94635-backport-94517-to-v11.3.x
revert-96078-fix-folder
revert-96146-ieva/update-gas-ft-status
revert-99553-selectors/add-alerting-selectors
revert-99689-release/13009094673/11.1.11
rjcrutch-scim-doc1
rm-bundled-plugins
rm-pluginsDetailsRightPanel-ft
robbymilo/fix-enterprise-broken-links
routing/explore-tests
routing/test
routing/update-history
row-repeat-v2
rows-layout
rtk-dashboards-v2
rtk-gen-test
rwwiv/alpha-rule-api
rwwiv/compare-decyrpted-contact-points
rwwiv/poc-sequential-eval
salvacorts/h11/loki-structured-metadata-autocompletion
samsch/add-feature-toggle-dev-helper-doc
sanitize-queries
santihernandezc/add_methods_merge_nflog_state
santihernandezc/json_templates_poc
santihernandezc/merge_remote_state
santihernandezc/merge_state_method
santihernandezc/missing_secure_setting_default_to_normal
santihernandezc/panic_eval_alert_rule_key_inconsistent_2
santihernandezc/update_alerting_package
santihernandezc/update_mimir_backend_image
sarahzinger/500missingvar
sarahzinger/970
sarahzinger/codeowner-experiments
sarahzinger/context-cancelled
sarahzinger/ds-metrics-in-querier
sarahzinger/querier-convert-errors
sarahzinger/querier-errors
sarahzinger/sql-expressions-feature
sarahzinger/test-break
sarahzinger/testing-ds-querier-with-enterprise
sbom-fix
sbom-fix-1
scgemav2-api-transformers
schemav2-api-2
schemav2-api-alpha2-followup
schemav2-api-ensure
schemav2-api-integration
schemav2-api-unify-resources
schemav2-bring-back-reverts
schemav2-fix-home-dashboard
schemav2-groupby-adhoc-breaking
schemav2-reset-unified-manager
schemav2-unify-layout-spec
schemav2/add-dry-run-types
scim-add-config-to-request-metadata
scim-usage-stats
scopes_support_dashes_in_scopenodes_find
search-fix-title-filter
search-folder-dashboard-remove-include-fields
search-shared-with-me
search-unified-allowed-kinds
search_performance_tests
secret-access-client
secret-mutation-hooks
secret-service/feature-branch
secret-service/outbox-with-dst
secret-service/outbox-with-dst-2
secrets-service/feature-branch-merge-main-13-12-24-1139
secrets/add-external-id-to-secure-value-status
secrets/base-encryption-manager
secrets/cleanup
secure-field-sketch
security/sbom-ci-fix
serge/add-ad-hoc-filter-combobox-collapse
serge/add-value-safeguard-in-auto-size-input
serge/await-load-before-restoring-scroll
serge/include-undefined-in-type-of-variable-query
serge/make-conditional-data-rule-reactive
serge/rework-tab-repeats
serge/scenes-react-router-test
serge/scenes-with-grafana-v11-test
serge/standartise-dashboard-ds-request-debounce
serge/test-scenes-update
serge/test-update-scenes-v11.3
serge/undo-conditional-rendering
service-user-provider
setup-live-reloading
shantanu/guided_sharding
show-info-for-sync
sidecar/add-initial-context
sidecar/aggregate-url-location
simpson-10.4.6-no-switch
simpson-1016-no-switch
simpson-fix-user-agent
simpson-query-service-sse
simpson-test-automation
simpson-test-mssql-merge
simpson-v11-mssql-kerberos
simpson-walkthrough-comments
single-top-nav-means-single
sj/adhoc-filter-barchart
sj/adhoc-filter-barchart-oneclick
sj/always-show-table-view
sj/cleanup-husky-works-on-macos
sj/dashboard-ds-adhoc-filter-numeric-fields
sj/dashboard-ds-implements-adhoc-filtering
sj/enable-sql-expressions
sj/enable-sql-expressions-locally
sj/first-signed-commit
sj/inline-table-view-of-the-data
sj/remove-transformationsVariableSupport-flag
sj/sql-expr-add-more-nodes
sj/sql-expr-bump-gms-to-fix-panic
sj/sql-expr-rename-vars
sj/sql-expr-support-more-types
sj/sql-expression-limits-squashed
sj/sql-expressions-improve-conversion-performance
sj/sql-expressions-list-allowed-funcs
sj/test-with-alerting/kb/sqlExprMultiTSFix
sj/testing-git-config
sjkb/sql-expression-limits-OLD
sknaumov/time-picker-custom-quick-ranges
slow
snyk-fix-ab30d0ad3a3f93b5a66f75333b76d84b
solo-panel-rethink
spike/git-sync-ui-webhook-implementation
split-read-write-service
sprinkles-api-serve
sqlExprCodeOwn
sriram/barchart-no-value-text
sriram/postgres-connectionstring
sriram/sqlds-macros-mysql
stars-as-collection
staton/panel-chrome-menu-icon
steady
stevesg/alerting-data-source-writer-feature
stevesg/alerting-dividing-api-package
stevesg/alerting-ha-redis-prefix
stevesg/backoff-for-alert-eval
stevesg/loki-structured-metadata
stevesg/recording-rule-uid-check
stevesg/tempo-alerting
stevesg/tempo-alerting-again
storage-backend-testsuite
storage-backend-use-testsuite
storage-with-authz
strict-csp-comment
submit-change-github
sunker/user-storage-refactor-poc
suntala/big-obj-rehydration-in-US
suntala/cleanup-k8s-folder-routes
suntala/configure-thresh-big-obj
suntala/dashboard-import-refresh-cache
suntala/disable-k8s-folder-create-temp
suntala/editing-provisioned-folder
suntala/fix-admin-login-name
suntala/fix-failing-build
suntala/fix-subfolder-create
suntala/folderservice-to-getalllibraryelements
suntala/folderservice-to-searchwherefilter
suntala/frontend-linting
suntala/get-authorizer
suntala/improved-get-create-folder
suntala/k8s-create-folder-frontend
suntala/large-history
suntala/large-history-cleaned-up
suntala/poc-deletion-of-provisioned-folder
suntala/poll-once-per-server
suntala/refactor-folder-creation-permissions-2
suntala/refactor-folder-prefixtests
suntala/set-folder-version-properly
suntala/test
suntala/test-2
suntala/test-create-resp
svennergr/add-function-observable
svennergr/change-explorations
svennergr/explore-the-sequel
svennergr/expose-sidebar-fns
svennergr/fail-soft-dashboard-macro
svennergr/hide-label
svennergr/hide-nav-when-plugin-disabled
svennergr/investigations-api
svennergr/llm-tools
svennergr/loki-feature-flag-removal
svennergr/opposite-approach
svennergr/resizeable-extension-sidebar
svennergr/settings-drilldown-links
svennergr/tmp-loki-header-add
swagger-csp
swagger-entry-point
table-filter-update
table-support-oneclick-datalink
tempo/update-ref
tempo/update_ref
test-APIs
test-api-interfaces
test-cve-detection-release-11.4.3
test-distroless-image
test-workflow
test/general-dashboards-scenes-e2e
testIntegration_AdminApiReencrypt-fix
theme-v12
time-series-customize-tooltip
timlevett/pills-wrap-it
titolins/add_remote_config_size_metric
titolins/fix-dingding-missing-url
titolins/patch-new-secure-fields-remote-am
titolins/patch-new-secure-fields-remote-am-simple
titolins/sync-flush-dispatch
titolins/sync-flush-time
titolins/test-tests
titolins/update-alerting-prom-am
tmp/intersection-observer
toddtreece/app-sdk-custom-routes
toddtreece/builder-versions
toddtreece/comparefunc
toddtreece/custom-route
toddtreece/dashboard-conversion-poc
toddtreece/dataplane-route-handler
toddtreece/delete-returns-full-obj
toddtreece/field-selector-support
toddtreece/fix-dashboard-conversion
toddtreece/fix-depguard
toddtreece/fix-test-symlinks
toddtreece/go-workspace-fix
toddtreece/improve-accesscontrol-tracing
toddtreece/k8s-client-tracing
toddtreece/plugin-sdk-runner
toddtreece/provisioning-external-id-fix
toddtreece/standalone-metric-handler
toddtreece/update-drone-workspace
toddtreece/update-go-duckdb
tom/foundation-sdk-docs
tonypowa/alerting-video
tonypowa/mute-timings-api
trace-view-css
transformation-filter-field-bug
translate-npm-packages
tskarhed/combobox/debounce-on-open
tskarhed/combobox/description-support
tskarhed/combobox/min-width
tskarhed/dynamic-heading-component
tskarhed/extractfieldtransform
tskarhed/multi-floating-ui
tskarhed/multi-virtual
tskarhed/performance/component-testing
tskarhed/scopes/selector/group
tskarhed/scopes/show-parent-command-palette
tskarhed/scss/buttons
tskarhed/storybook-performance-poc
tskarhed/tabs-numberings
tweak-toolbar-checkbox
unauthenticated-apiserver-access
undef1nd/flag-grafanaconThemes
undef1nd/ofrep-testing
undef1nd/openfeature-api
undef1nd/prov-dash-to-subfolders
undef1nd/remove-flag-kubernetesPlaylists
undef1nd/resolve-conflicts
unified-folder-tree
unified-search-exploration
unified-search-refactor
unified-split-bleve-index
unified-split-document-builder
unified-storage-add-log-for-watch-latency
unified-storage-bench
unified-storage-dashboard-provisioning-retry-when-dashboard-not-found
unified-storage-read-after-write-k8s-client
unified_storage/dw_error
unified_storage/readme
unistore-add-shard
unistore-distributor-option2
unistore-fix-integration-test
unistore-folders-fix-writing-folders-is-not-supported
unistore-folders-poc
unistore-onboarding-folders-update-folder-endpoint
unistore-refactor-client-provider
unistore-remove-dead-code-and-fix-registerer
unistore-remove-file-backend-support
unistore-ring-config
unistore/fail_check
unistore_force_uuid
update-deps-axios
update-generic-strategy
update-go-comments-style-link
update-grafana-aws-sdk-1
update-health-status
update-moby
update-ol-deps
update-swagger
update-xlsx
upgrade-ol-10
upgrade_sdk_0_240_0
use-authlib-info
use-generation-to-prune
use-manager-annotations
use-setup-steps
using-window-function
v0.0.x
v1.8.x
v10.0.x
v10.1.x
v10.1.x-upGoCrypto
v10.2.x
v10.2.x-DEPRECATED
v10.3.x
v10.3.x-fix-go-format
v10.4.x
v11.0.x
v11.1.x
v11.2.x
v11.3.x
v11.4.x
v11.5.x
v2.0.x
v2.1.x
v2.6.x
v3.0.x
v3.1.x
v4.0.x
v4.1.x
v4.2.x
v4.3.x
v4.4.x
v4.5.x
v4.6.x
v4.7.x
v5.0.x
v5.1.x
v5.2.x
v5.3.x
v5.4.x
v6.0.x
v6.1.x
v6.2.x
v6.3.0
v6.3.x
v6.4.x
v6.5.x
v6.6.x
v6.7.x
v7.0.x
v7.1.x
v7.2.x
v7.3.x
v7.3.x-alt
v7.4.x
v7.4.x-alt
v7.5.x
v7.5.x-settings-provider
v8-theme2
v8.0.x
v8.1.x
v8.2.x
v8.2.x-drone-test
v8.2.x-sync
v8.3.0beta1
v8.3.x
v8.3.x_upgrade_grabpl
v8.4.x
v8.5.x
v9.0.x
v9.1.x
v9.2.x
v9.3.x
v9.4.0-beta1-fix
v9.4.x
v9.5.x
var-option-undo-redo
vizards_ad_hoc_viz2
vt/oauth_errors
vt/saml_doc
vt/session_popup
vt/sso_ui
w1kman/secrets-management-admin-ui
watch-over-live
watch-over-live-take-2
wb/fix-140
wb/plugin-install-foo
webhook-in-status
what-changed
whats-new-v12.1
wip-streaming-loki-queries
with-classic-type
with-more-tests-mmandrus/bulk-result-update
yaelle/poc-rs-force-type-definition
yaelle/poc-rs-force-type-definition-v2
yesoreyeram/zipkin-backend-migration
yjsong/mssql-fe
yuri-tceretian/alerting-update-module-branch
yuri-tceretian/contact-points-v2
yuri-tceretian/exploreFn
yuri-tceretian/merge-secrets-remote-alertmanager
yuri-tceretian/new-expr
yuri-tceretian/noop-contactpoint-provision
yuri-tceretian/user-grafana-config-refactor
ywzheng1/delete-provisioned-dashboard-from-new-branch
ywzheng1/git-sync-bulk-delete
ywzheng1/git-sync-bulk-move-resources
ywzheng1/git-sync-ui-bulk-move-provision-resources
ywzheng1/git-sync-usedefaultvalues-hook-return-safe-default-values
ywzheng1/test-docker
ywzheng1/time-picker-with-history-improve-type-handling
ywzheng1/timepicker-add-local-browser-time-info-when-on-hover
zanzana/capabilities-api
zanzana/fix-mysql
zanzana/folder-subresources
zanzana/healthcheck-non-tls
zanzana/mysql-fixes
zanzana/permission-sync
zanzana/refactor-client
zanzana/test-dashboard-search
zoesyc-influx-config-docs
zserge/cgoaway
zserge/devenv-spanner
zserge/golint-yml
zserge/lock-drone-yml
zserge/remove-drone-cronjobs
zserge/shard-tests
zserge/sqlite-wasm
zserge/teams-ids
zserge/xorm-core
zserge/xorm-core-2
1.0.0
6.1.6
7.0.0
7.2.1
dupa
list
omgtest
packages@6.3.0-alpha.33
packages@6.3.0-alpha.36
packages@6.3.0-beta.1
pkg/promlib/v0.0.1
pkg/promlib/v0.0.2
pkg/promlib/v0.0.3
pkg/promlib/v0.0.4
pkg/promlib/v0.0.5
pkg/promlib/v0.0.6
pkg/promlib/v0.0.7
pkg/promlib/v0.0.8
pkg/util/xorm/v0.0.1
pull
test
v0.0.0-cloud
v0.0.0-kmdagger1
v0.0.0-kmdagger2
v0.0.0-kmdagger3
v0.0.0-test
v0.0.0-test.2
v0.0.0-testrgm3
v0.0.0-testrgm4
v0.0.0-testrgm6
v0.0.1-test
v0.0.85-test
v1.0
v1.0.1
v1.0.2
v1.0.3
v1.0.4
v1.1.0
v1.2.0
v1.3.0
v1.4.0
v1.5.0
v1.5.1
v1.5.2
v1.5.3
v1.5.4
v1.6.0
v1.6.1
v1.7.0
v1.7.0-rc1
v1.8.0
v1.8.0-rc1
v1.8.1
v1.9.0
v1.9.0-rc1
v1.9.1
v10.0.0
v10.0.0-preview
v10.0.1
v10.0.10
v10.0.11
v10.0.12
v10.0.13
v10.0.2
v10.0.3
v10.0.4
v10.0.5
v10.0.6
v10.0.8
v10.0.9
v10.1.0
v10.1.1
v10.1.10
v10.1.2
v10.1.4
v10.1.5
v10.1.6
v10.1.7
v10.1.8
v10.1.9
v10.2.0
v10.2.1
v10.2.2
v10.2.3
v10.2.4
v10.2.5
v10.2.6
v10.2.7
v10.2.8
v10.2.9
v10.3.0
v10.3.1
v10.3.10
v10.3.11
v10.3.12
v10.3.3
v10.3.4
v10.3.5
v10.3.6
v10.3.7
v10.3.8
v10.3.9
v10.4.0
v10.4.1
v10.4.10
v10.4.11
v10.4.12
v10.4.13
v10.4.14
v10.4.15
v10.4.16
v10.4.17
v10.4.17+security-01
v10.4.18
v10.4.18+security-01
v10.4.19
v10.4.19+security-01
v10.4.2
v10.4.3
v10.4.4
v10.4.5
v10.4.6
v10.4.7
v10.4.8
v10.4.9
v11.0.0
v11.0.0-preview
v11.0.1
v11.0.10
v11.0.11
v11.0.2
v11.0.3
v11.0.4
v11.0.5
v11.0.5+security-01
v11.0.6
v11.0.6+security-01
v11.0.7
v11.0.8
v11.0.9
v11.1.0
v11.1.1
v11.1.10
v11.1.11
v11.1.12
v11.1.13
v11.1.2
v11.1.3
v11.1.4
v11.1.5
v11.1.6
v11.1.6+security-01
v11.1.7
v11.1.7+security-01
v11.1.8
v11.1.9
v11.1.999-zserge-test
v11.2.0
v11.2.1
v11.2.1+security-01
v11.2.10
v11.2.10+security-01
v11.2.2
v11.2.2+security-01
v11.2.3
v11.2.3+security-01
v11.2.4
v11.2.5
v11.2.6
v11.2.7
v11.2.8
v11.2.8+security-01
v11.2.9
v11.2.9+security-01
v11.3.0
v11.3.0+security-01
v11.3.1
v11.3.2
v11.3.3
v11.3.4
v11.3.5
v11.3.5+security-01
v11.3.6
v11.3.6+security-01
v11.3.7
v11.3.7+security-01
v11.3.8
v11.3.8+security-01
v11.4.0
v11.4.1
v11.4.2
v11.4.3
v11.4.3+security-01
v11.4.4
v11.4.4+security-01
v11.4.5
v11.4.5+security-01
v11.4.6
v11.4.6+security-01
v11.5.0
v11.5.1
v11.5.2
v11.5.3
v11.5.3+security-01
v11.5.4
v11.5.4+security-01
v11.5.5
v11.5.5+security-01
v11.5.6
v11.5.6+security-01
v11.6.0
v11.6.0+security-01
v11.6.1
v11.6.1+security-01
v11.6.2
v11.6.2+security-01
v11.6.3
v11.6.3+security-01
v12.0.0
v12.0.0+security-01
v12.0.1
v12.0.1+security-01
v12.0.2
v12.0.2+security-01
v2.0.0-beta1
v2.0.0-beta3
v2.0.1
v2.0.2
v2.1.0
v2.1.1
v2.1.2
v2.1.3
v2.5.0
v2.6.0
v2.6.0-beta1
v3.0-beta1
v3.0-beta2
v3.0-beta3
v3.0-beta4
v3.0-beta5
v3.0.0-beta6
v3.0.0-beta7
v3.0.1
v3.0.2
v3.0.3
v3.0.4
v3.1.0
v3.1.0-beta1
v3.1.1
v3.2.1-test
v4.0.0
v4.0.0-beta1
v4.0.0-beta2
v4.0.1
v4.0.2
v4.1.0
v4.1.0-beta1
v4.1.1
v4.1.2
v4.2.0
v4.2.0-beta1
v4.3.0
v4.3.0-beta1
v4.3.1
v4.3.2
v4.4.0
v4.4.1
v4.4.2
v4.4.3
v4.5.0
v4.5.0-beta1
v4.5.1
v4.5.2
v4.6.0
v4.6.0-beta1
v4.6.0-beta2
v4.6.0-beta3
v4.6.1
v4.6.2
v4.6.3
v4.6.4
v4.6.5
v5.,2.4
v5.0.0
v5.0.0-beta1
v5.0.0-beta2
v5.0.0-beta3
v5.0.0-beta4
v5.0.0-beta5
v5.0.1
v5.0.2
v5.0.3
v5.0.4
v5.1.0
v5.1.0-beta1
v5.1.1
v5.1.2
v5.1.3
v5.1.4
v5.1.5
v5.2.0
v5.2.0-beta1
v5.2.0-beta2
v5.2.0-beta3
v5.2.1
v5.2.2
v5.2.3
v5.2.4
v5.2.5
v5.3.0
v5.3.0-beta1
v5.3.0-beta2
v5.3.0-beta3
v5.3.1
v5.3.2
v5.3.3
v5.3.4
v5.4.0
v5.4.0-beta1
v5.4.1
v5.4.2
v5.4.3
v5.4.4
v5.4.4_private
v5.4.5
v6.0.0
v6.0.0-beta1
v6.0.0-beta2
v6.0.0-beta3
v6.0.1
v6.0.2
v6.1.0
v6.1.0-beta1
v6.1.1
v6.1.2
v6.1.3
v6.1.4
v6.1.6
v6.2.0
v6.2.0-beta1
v6.2.0-beta2
v6.2.1
v6.2.2
v6.2.3
v6.2.4
v6.2.5
v6.3.0
v6.3.0-alpha.30
v6.3.0-beta.0
v6.3.0-beta1
v6.3.0-beta2
v6.3.0-beta3
v6.3.0-beta4
v6.3.1
v6.3.2
v6.3.3
v6.3.4
v6.3.5
v6.3.6
v6.3.7
v6.4.0
v6.4.0-beta1
v6.4.0-beta2
v6.4.1
v6.4.2
v6.4.3
v6.4.4
v6.4.5
v6.5
v6.5.0
v6.5.0-beta1
v6.5.1
v6.5.2
v6.5.3
v6.6.0
v6.6.0-beta1
v6.6.1
v6.6.2
v6.7.0
v6.7.0-beta1
v6.7.1
v6.7.2
v6.7.3
v6.7.4
v6.7.5
v6.7.6
v7.0.0
v7.0.0-beta1
v7.0.0-beta2
v7.0.0-beta3
v7.0.1
v7.0.2
v7.0.3
v7.0.4
v7.0.5
v7.0.6
v7.1.0
v7.1.0-beta1
v7.1.0-beta2
v7.1.0-beta3
v7.1.1
v7.1.2
v7.1.3
v7.1.4
v7.1.5
v7.2.0
v7.2.0-beta1
v7.2.0-beta2
v7.2.1
v7.2.2
v7.2.3
v7.3.0
v7.3.0-beta1
v7.3.0-beta2
v7.3.1
v7.3.10
v7.3.2
v7.3.3
v7.3.4
v7.3.5
v7.3.6
v7.3.7
v7.3.8
v7.4.0
v7.4.0-beta1
v7.4.1
v7.4.2
v7.4.3
v7.4.4
v7.4.5
v7.5.0
v7.5.0-beta1
v7.5.0-beta2
v7.5.1
v7.5.10
v7.5.11
v7.5.12
v7.5.13
v7.5.15
v7.5.16
v7.5.17
v7.5.2
v7.5.3
v7.5.4
v7.5.5
v7.5.6
v7.5.7
v7.5.8
v7.5.9
v8.0.0
v8.0.0-beta1
v8.0.0-beta2
v8.0.0-beta3
v8.0.1
v8.0.2
v8.0.3
v8.0.4
v8.0.5
v8.0.6
v8.0.7
v8.1.0
v8.1.0-beta1
v8.1.0-beta2
v8.1.0-beta3
v8.1.1
v8.1.2
v8.1.3
v8.1.4
v8.1.5
v8.1.6
v8.1.7
v8.1.8
v8.2.0
v8.2.0-beta1
v8.2.0-beta2
v8.2.1
v8.2.2
v8.2.3
v8.2.4
v8.2.5
v8.2.6
v8.2.7
v8.3.0
v8.3.0-beta1
v8.3.0-beta2
v8.3.1
v8.3.10
v8.3.11
v8.3.2
v8.3.3
v8.3.4
v8.3.5
v8.3.6
v8.3.7
v8.4.0
v8.4.0-beta1
v8.4.1
v8.4.10
v8.4.11
v8.4.2
v8.4.3
v8.4.4
v8.4.5
v8.4.6
v8.4.7
v8.5.0
v8.5.0-beta1
v8.5.1
v8.5.10
v8.5.11
v8.5.13
v8.5.14
v8.5.15
v8.5.16
v8.5.2
v8.5.20
v8.5.21
v8.5.22
v8.5.24
v8.5.26
v8.5.27
v8.5.3
v8.5.4
v8.5.5
v8.5.6
v8.5.9
v9.0.0
v9.0.0-beta1
v9.0.0-beta2
v9.0.0-beta3
v9.0.1
v9.0.2
v9.0.3
v9.0.4
v9.0.5
v9.0.6
v9.0.7
v9.0.8
v9.0.9
v9.1.0
v9.1.0-beta1
v9.1.1
v9.1.2
v9.1.3
v9.1.4
v9.1.5
v9.1.6
v9.1.7
v9.1.8
v9.2.0
v9.2.0-279c6c6c7d
v9.2.0-beta1
v9.2.1
v9.2.10
v9.2.13
v9.2.15
v9.2.17
v9.2.18
v9.2.19
v9.2.2
v9.2.20
v9.2.3
v9.2.4
v9.2.5
v9.2.6
v9.2.7
v9.2.8
v9.3.0
v9.3.0-beta1
v9.3.1
v9.3.11
v9.3.13
v9.3.14
v9.3.15
v9.3.16
v9.3.2
v9.3.4
v9.3.6
v9.3.8
v9.4.0
v9.4.0-beta1
v9.4.1
v9.4.10
v9.4.12
v9.4.13
v9.4.14
v9.4.15
v9.4.17
v9.4.2
v9.4.3
v9.4.7
v9.4.9
v9.5.0
v9.5.1
v9.5.10
v9.5.12
v9.5.13
v9.5.14
v9.5.15
v9.5.16
v9.5.17
v9.5.18
v9.5.19
v9.5.2
v9.5.20
v9.5.21
v9.5.3
v9.5.5
v9.5.6
v9.5.7
v9.5.8
v9.5.9
vtest-new-release-pipeline